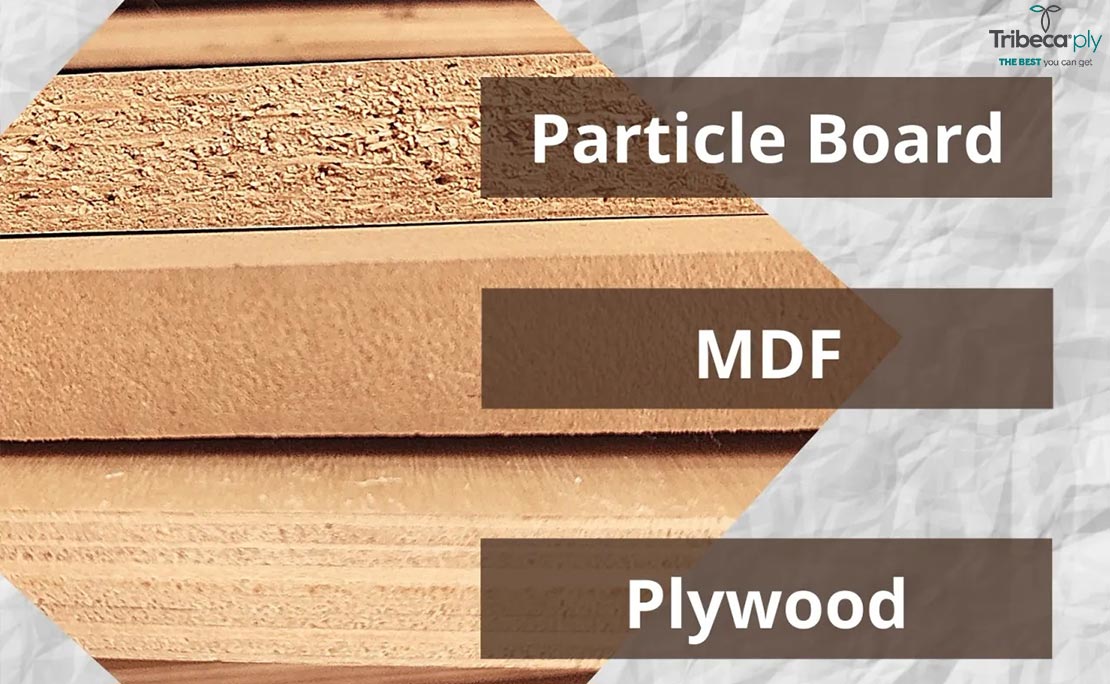
When it comes to choosing the right wood product for various construction and woodworking projects, several options are available. Plywood, Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF), and Particleboard are three popular choices among engineered wood products. Each material has its unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions and achieving the best results for your specific project.
Plywood:
Advantages:
- Strength and Durability: Plywood is made by gluing together layers of veneer, which are cross-laminated to create a strong and stable sheet. This construction makes plywood highly durable and resistant to warping or splitting, even in varying weather conditions.
- Versatility: Plywood is available in various grades, thicknesses, and sizes, making it versatile for a wide range of applications. It is commonly used in construction, furniture making, cabinetry, and flooring.
- Aesthetics: The natural wood grain appearance of plywood makes it suitable for projects where the exposed surface is desired. It can be stained or painted, providing flexibility in achieving the desired aesthetics.
- Structural Integrity: Plywood’s cross-laminated structure gives it excellent strength and load-bearing capacity, making it suitable for applications that require stability and structural support.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: Plywood can be relatively more expensive compared to MDF and particleboard, especially for higher-grade varieties.
- Susceptible to Moisture: Although exterior-grade plywood is available for outdoor use, regular plywood is still prone to moisture damage if not adequately sealed or protected.
MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard):
Advantages:
- Smooth Surface: MDF is made from wood fibers bonded with resin under high pressure and temperature, resulting in a smooth and consistent surface, free from knots or imperfections.
- Affordability: MDF is generally more budget-friendly than plywood and can be a cost-effective choice for projects with tight budgets.
- Versatility in Finishing: The smooth surface of MDF is ideal for painting, veneering, or laminating, offering a wide range of finishing options.
- Stability: MDF has excellent dimensional stability, making it less prone to expansion and contraction due to changes in humidity and temperature.
Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to Moisture: MDF is highly susceptible to water damage and should not be used in areas with high humidity or exposure to moisture.
- Limited Load-Bearing Capacity: MDF is not as structurally strong as plywood and is more suitable for non-load-bearing applications.
Particleboard:
Advantages:
- Affordability: Particleboard is the most economical option among the three, making it popular for budget-conscious projects.
- Smooth Surface: Like MDF, particleboard also has a smooth surface, making it suitable for painting or laminating.
- Recyclability: Particleboard is often made from recycled wood particles, making it an environmentally friendly choice.
Disadvantages:
- Moisture Vulnerability: Particleboard is highly susceptible to moisture and can swell or disintegrate when exposed to water.
- Weakness: Particleboard is not as strong as plywood or MDF and is prone to sagging or breaking under heavy loads.
- Limited Use: Particleboard is best suited for non-structural, interior applications and may not be suitable for demanding projects that require strength and durability.
When choosing between plywood, MDF, and particleboard, consider the project requirements, budget, and the environment in which the material will be used. Properly assessing these factors will help you make an informed decision and ensure the success of your construction or woodworking endeavors.